Analysis of Cannabis sativa L. leaves by ambient mass spectrometry
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36524/ric.v9i3.2184Keywords:
canabinoides, espectrometria de massas ambiente, leaf spray ionizationAbstract
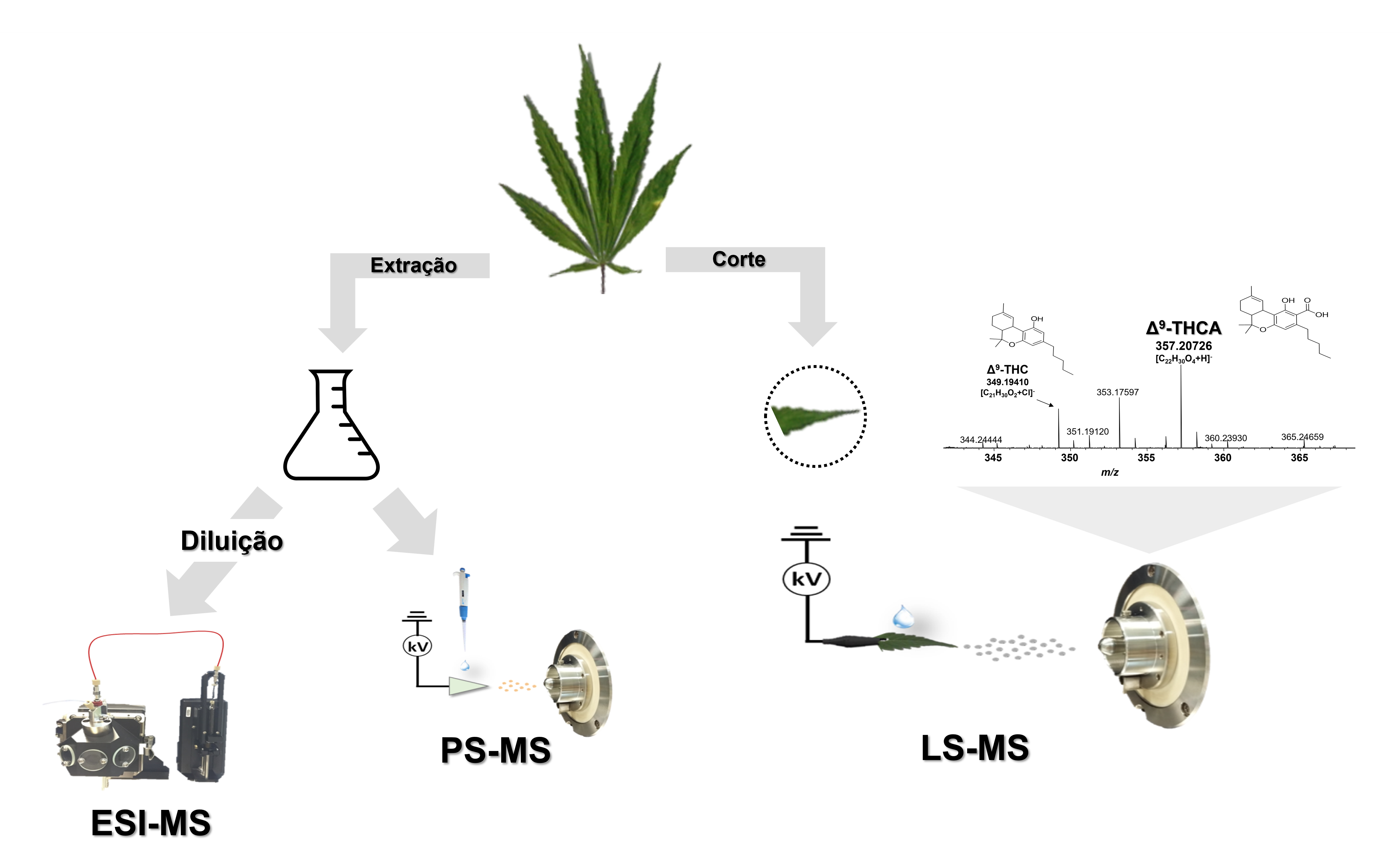
The Cannabis plant has had a very close relationship with society for many years, whether due to its cultural and/or medicinal use, as well as the use of its derivative products (such as marijuana and hashish) for recreational purposes. Regardless of the purpose of use, the fast and efficient identification of Cannabis must be achieved by the detection of compounds of its main class: the cannabinoids. In this sense, the present work presents an alternative of fast analysis and with a reduced matrix effect using Ambient Mass Spectrometry techniques: with paper spray (PS) and leaf spray ionization (LS) sources and comparing them with the Atmospheric Pressure Ionization technique (API): using electrospray ionization (ESI) source. All sources proved to be adequate in the ionization process of the target class: cannabinoids. However, the LS-MS technique exhibited greater relative intensity and a smaller ionic suppression effect, indicating it as a promising tool for the rapid detection of cannabinoids directly from plant tissue, eliminating the extraction and dilution steps required in the other presented sources.Keywords: cannabinoids; ambient mass spectrometry; leaf spray ionization.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista Ifes Ciência

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
b. Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


